In the realm of landscaping and gardening in Australia, the strategic use of garden hedges is an art that transforms outdoor spaces into refined extensions of the home. At 2 Men and a Shovel, we understand the significance of well-chosen and meticulously maintained garden hedges. In this guide, we will delve into the process of selecting the right hedge species, providing valuable insights into proper planting methods and effective maintenance practices.
Choosing the Right Hedge Species
Selecting the appropriate hedge species is an important decision that influences the overall aesthetic and functionality of the outdoor space. In the diverse Australian climate, it’s crucial to consider factors such as soil type, sunlight exposure, and water availability.
Climate Considerations
Australia’s climatic diversity demands a thoughtful approach to hedge selection. Coastal regions with salt-laden winds, for example, necessitate hedges with salt tolerance. On the other hand, inland areas with extreme temperatures may require drought-resistant varieties.
Height and Density
The purpose of the hedge – whether it’s to create privacy, define boundaries, or serve as a windbreak – influences the ideal height and density. Photinia, Murraya, and Buxus are popular choices for creating dense privacy screens, while Westringia or Correa are well-suited for lower, more decorative hedges.
Soil Compatibility
Assessing soil conditions is imperative for the health and longevity of hedges. Conducting soil tests helps determine pH levels, drainage capacity, and nutrient composition. Species like Escallonia or Griselinia adapt well to a range of soil types, making them versatile choices for various landscapes.
Proper Planting Techniques
Once the ideal hedge species is chosen, proper planting techniques become instrumental in ensuring successful establishment and long-term health.
Site Preparation
Begin by clearing the designated area of any debris, weeds, or unwanted vegetation. Enhance soil quality by incorporating organic matter, such as well-rotted compost, to promote nutrient retention and improve drainage.
Spacing and Layout
Carefully plan the spacing between individual hedge plants, considering their mature size. Proper spacing encourages adequate airflow and sunlight penetration, reducing the risk of diseases and promoting uniform growth.
Planting Depth and Watering
Plant hedge specimens at the correct depth, ensuring the root ball is level with the soil surface. Thoroughly water the newly planted hedges and maintain a consistent watering schedule during the initial establishment phase. Mulching around the base helps retain soil moisture and suppress weed growth.
Types of plants for hedges in Australia
Lilly Pilly (Syzygium spp.)
Lilly Pilly, a versatile native Australian plant, is renowned for its suitability in creating dense and resilient hedges. With glossy evergreen foliage and a range of cultivars offering varying leaf sizes and colours, Lilly Pilly adds an aesthetic charm to outdoor spaces. Its adaptability to different soil types and climates, coupled with the ability to withstand coastal conditions, makes it an ideal choice for both urban and coastal landscapes. The plant’s rapid growth and response to pruning allow for the creation of well-defined and visually appealing hedges that offer privacy and act as a robust windbreak.
Westringia (Westringia spp.)
Westringia, commonly known as the Australian Rosemary, is a hardy and low-maintenance option for garden hedges. Characterised by small, aromatic leaves and a compact growth habit, Westringia imparts a Mediterranean feel to landscapes. Its drought tolerance and adaptability to various soil types, including coastal sands, make it a reliable choice for Australian gardens. With minimal pruning, Westringia forms a neat and tidy hedge, providing both structure and texture to outdoor settings. The plant’s ability to thrive in full sun or partial shade enhances its versatility in landscaping projects.
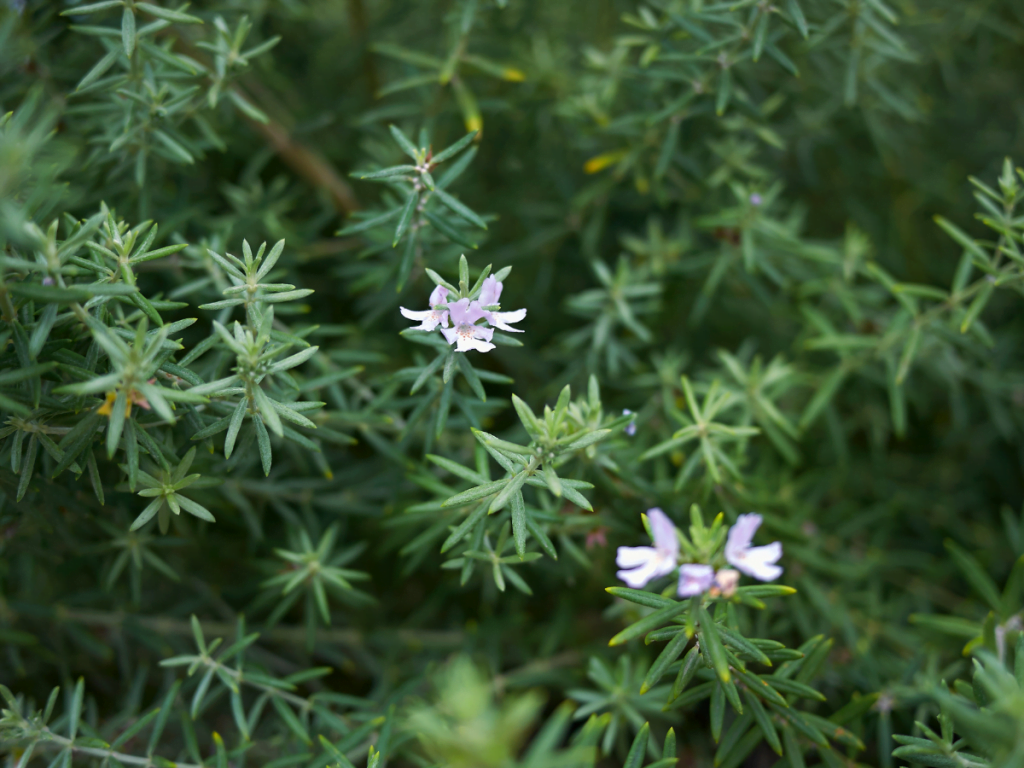

Murraya (Murraya paniculata)
Murraya, also known as Orange Jessamine, stands out as a popular choice for hedging in Australia, prized for its fragrant flowers and lush, dark green foliage. This evergreen shrub thrives in subtropical and tropical regions, making it well-suited for various climates across the country. Murraya’s dense growth habit and rapid growth make it an excellent option for creating effective privacy screens and decorative borders. Regular pruning enhances its bushy appearance, and its resistance to pests and diseases contributes to its overall hardiness, ensuring a long-lasting and visually appealing hedge.
Griselinia (Griselinia littoralis)
Griselinia, commonly known as New Zealand Broadleaf, is a popular choice for hedging, celebrated for its vibrant green, leathery leaves and robust growth. Suitable for a range of soil types and adaptable to both full sun and partial shade, Griselinia is well-suited for diverse Australian landscapes. Its moderate growth rate allows for efficient hedge formation, while its tolerance to coastal conditions makes it an excellent choice for seaside gardens. With minimal maintenance requirements and the ability to withstand wind exposure, Griselinia contributes to the creation of lush and enduring hedges that enhance the visual appeal of outdoor spaces.
Effective Maintenance Practices
Regular maintenance is the key to preserving the aesthetic appeal and functionality of garden hedges.
Pruning Techniques
Pruning is an art that shapes the hedge and promotes healthy growth. Regular, light pruning encourages dense foliage and maintains a neat appearance. However, excessive pruning should be avoided, as it may stress the plants and compromise their overall vitality.
Pest and Disease Management
Monitor hedges for signs of pests and diseases, addressing issues promptly to prevent their spread. Without careful management, pests can get out of control. If you’re time poor, it’s always recommended that you find a gardener near you to help manage pests before they become a problem.
Fertilisation and Nutrient Management
Periodic fertilisation is essential to ensure hedges receive the necessary nutrients for robust growth. Conduct soil tests to identify nutrient deficiencies, and tailor fertilisation schedules accordingly.
Watering Practices
Implementing a consistent watering routine is critical, especially during dry periods. Consider the specific water requirements of the chosen hedge species, and adjust irrigation schedules accordingly. Drip irrigation systems or soaker hoses can efficiently deliver water directly to the root zone.